 In 1804, President Thomas Jefferson sent Meriwether Lewis, William Clark, and a team of men on a vital mission to explore the wild, unmapped West. Lewis brought his dog along. According to journals kept by several of the explorers, the dog helped a lot. He retrieved animals that had been shot for food. He scared away grizzly bears, and a bull bison that charged into camp. The old journal pages are often hard to read, and this led to a misunderstanding of the dog's name. People thought that he was called Scannon. Not until 1985 did a historian carefully examine every mention of the dog. He found that Lewis had actually named the dog Seaman. The dog was a Newfoundland, a breed often kept on ships. They are great swimmers, and could save people from drowning. In the expedition's journals, Seaman was last mentioned in July, 1806, two months before the explorers returned from the West and reached the little town of St. Louis on the Mississippi River. After that, there is no word about the dog in letters or reports written by Lewis, Clark, or others. The mystery of what happened to Seaman was solved in the year 2000, thanks to the work of historian James Holberg. He had found a book, written in 1814 by historian Timothy Alden, which told of a little museum in Virginia. Alden found a dog collar displayed there that William Clark had given to the museum. On the collar were these words: "The greatest traveller of my species. My name is SEAMAN, the dog of captain Meriwether Lewis, whom I accompanied to the Pacifick ocean through the interior of the continent of North America." The collar was later destroyed by fire, but in his 1814 book Timothy Alden also wrote further details about Seaman. Historians report that after the expedition, Meriwether Lewis' life became one of failure and despair. In October 1809 he took his own life. Alden wrote that Seaman was there when Lewis was buried, and "refused to take every kind of food, which was offered to him, and actually pined away and died with grief upon his master's grave." People who know Newfoundland dogs say that this could be true, because these dogs are fiercely loyal to their owners. Unless historians find some new evidence, that is how the life of this great dog hero ended. 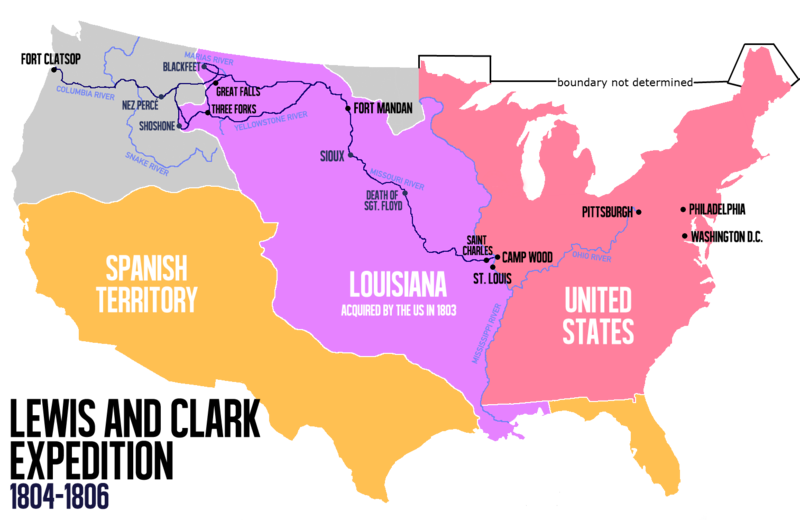 The Lewis and Clark Expedition was the first American expedition to cross what is now the western portion of the United States, departing in May 1804, from near St. Louis on the Mississippi River, making their way westward through the continental divide to the Pacific coast. Seaman was along on every bit of the round trip expedition of over seven thousand miles. However, like the explorers, he traveled many of those miles on a keel boat or canoe--up the Missouri and other rivers, downstream to the Pacific Ocean, and then the return journey to St. Louis in 1806.  Laurence Pringle has written a book about Seaman. This richly detailed account of the Lewis and Clark expedition includes its planning, its adventures and discoveries, and its aftermath. With intriguing sidebars, historical illustrations, journal excerpts, and original art, this account of what became known as the Corps of Discovery features the remarkable dog that was the expedition's most unusual member. For more information click here. MLA 8 Citation
Pringle, Laurence. "Did the Hero Dog Survive?" Nonfiction Minute, iNK Think Tank, 29 Jan. 2018, www.nonfictionminute.org/the-nonfiction-minute/ did-the-hero-dog-survive.
2 Comments
 Almost every spring an amazing event in nature happens in parts of the United States. Huge numbers of insects called periodical cicadas emerge from the soil. For a few weeks they fill the days with loud buzzing calls. Every summer you can hear the calls of some kinds of cicadas, but periodical cicadas are different. They exist only in the eastern two-thirds of the United States, and have the longest of all insect lives. Some periodical cicadas live 13 years, others 17 years, with nearly all of that time spent underground. Young cicadas, called nymphs, sip water and nutrients from tree roots. The nymphs count the years, probably by sensing changes in tree sap, as it is affected by the seasons of each year. When their countdown ends and soil warms in the spring, millions of cicada nymphs dig out. They climb posts, bushes, and trees, and cling there. Their nymph "skins" split open and adult cicadas wriggle free. Finally, after many years underground, they are out in the sunshine. They can fly, and the buzzing noises of males attract females. It is a noisy and hectic time in their lives. They have just a few weeks to mate and produce the next generation. Once females lay eggs in tree twigs, all of the adults die. Soon after, tiny nymphs hatch from the eggs. They drop to the soil, borrow in, and begin to sip juices from tree roots. The nymphs grow slowly, counting the years until they will have their own time in the sun. Nearly every year, one or more populations, called broods, of periodical cicadas emerge. Seventeen year cicadas live mostly in the Northeast and Upper Midwest. Thirteen year cicadas are most common in the South and Lower Midwest. Some broods emerge in parts of just a few states. Some years, a more widespread brood emerges in parts of fifteen states. Notice that I say "parts" of states. These cicadas don't roam around. The nymphs go underground in the same places where their parents emerged. You will find them in one town but not another, in one neighborhood but not another. Some people call cicadas "locusts," but locusts are a kind of grasshopper that eats plants. Cicadas do not chew on plants. They are harmless, fascinating creatures. And, once in a great while, they give us a rare and awe-inspiring animal spectacle.  Visit the great website, Cicadamania, which has high praise for this book: "Definitely the best cicada book for kids. Adults will appreciate it as well, as it is well written, factually accurate, and beautifully illustrated." You can read more about Larry's fascination for these creatures on his website. MLA 8 Citation
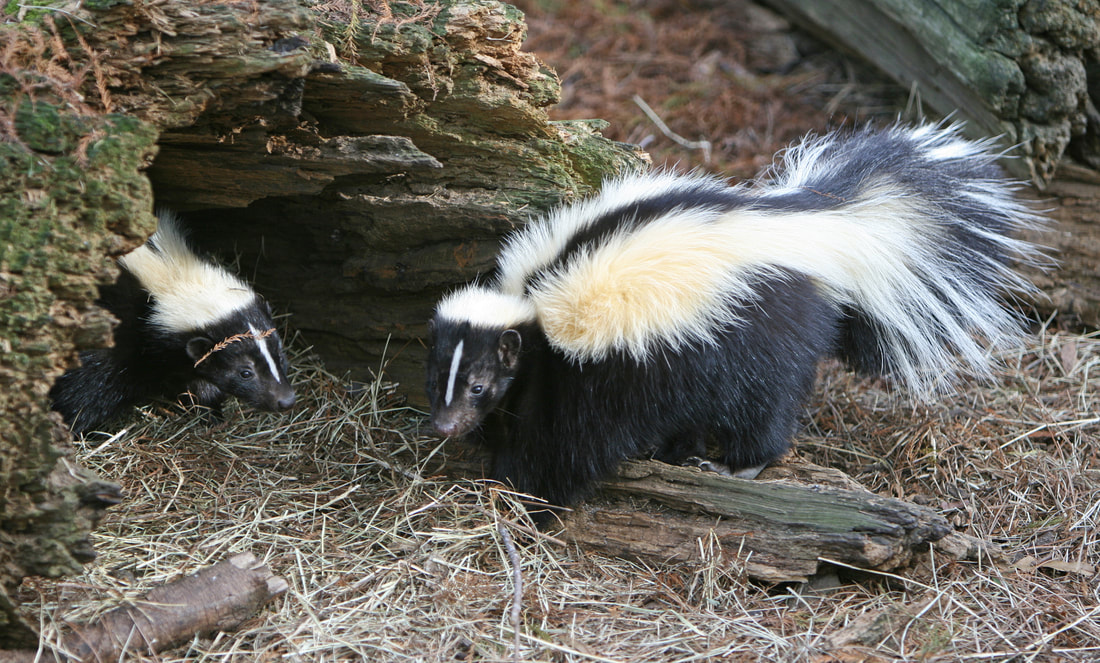
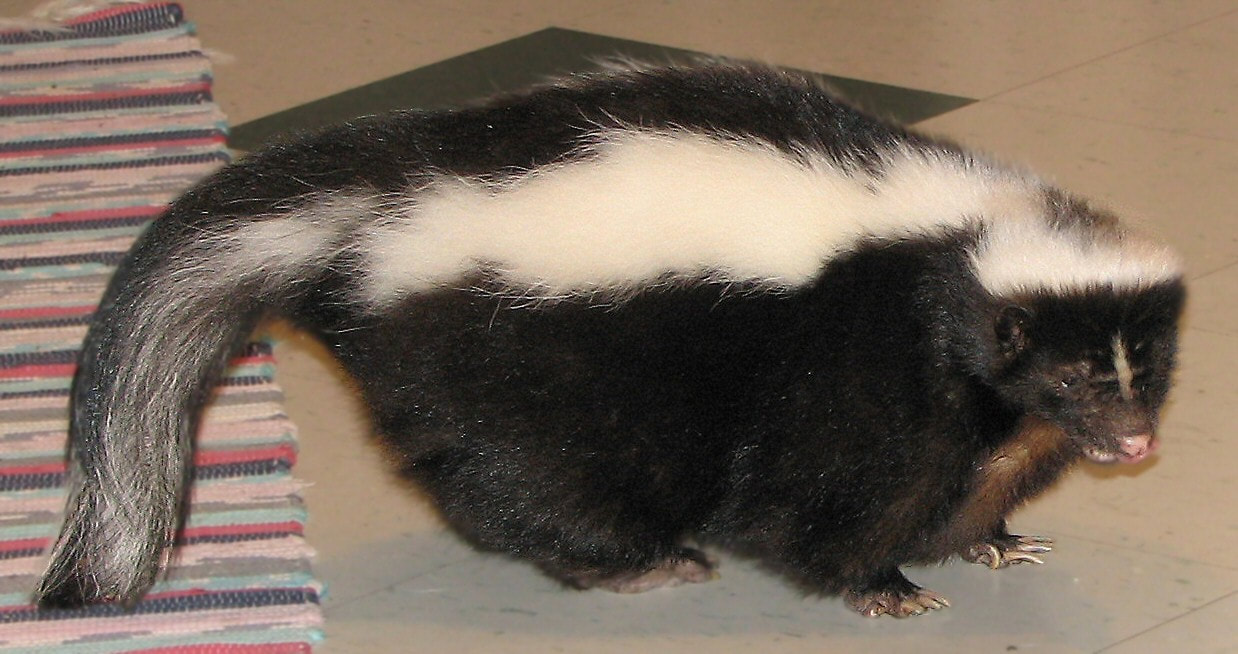
Pringle, Laurence. "Here Come the Cicadas." Nonfiction Minute, iNK Think Tank, 23 Apr. 2018, www.nonfictionminute.org/the-nonfiction-minute/ Here-Come-the-Cicadas. Are skunks aggressive, dangerous animals? Or are they peaceful animals that try to avoid trouble? Well, biologists who study skunks think of them this way: if life were a sport, skunks would be known for their strong defense and for playing fair. Skunk stinkiness comes from a chemical weapon called musk. Foxes, weasels, and some other mammals also produce musk, but skunk musk is especially strong and long-lasting. And only skunks use musk to defend themselves from attack. Picture a skunk ambling along in the night, looking for food. It digs in the soil to get tasty earthworms and beetle grubs. The black and white fur that comes with just being a skunk sends a warning. This color pattern is unusual among mammals. It signals: "Beware, don't mess with me!" Suppose a coyote or other predator ignores this first warning. It steps toward the skunk. When a skunk feels threatened, it faces the danger. It raises its tail and tries to look as big as possible. It stamps its feet and clicks its teeth together. It may growl or hiss. Oh, oh! Despite all of these warnings, the coyote growls and comes closer. Now the skunk gets really serious. It twists its body into a U-shape, so it can see the coyote and also aim its rear end toward it. The skunk's tail arches over its back, away from its rear—the final warning. This gives the skunk a clear shot, and also protects its own fur from the stinky musk. Skunks try to avoid smelling bad! From two grape-sized glands, a skunk can spray musk as a fine mist, or squirt a stream. It can squirt accurately for about 12 feet (3.7m), and hit an attacking animal right in the face. The musk stings the predator's eyes, and can blur its vision for a while. And it stinks! Animals hit with this musk learn to never bother a skunk again. A skunk's glands store enough musk to fire a half dozen shots but then need a week or so to produce more. This is seldom a problem, since a skunk sprays only when its life seems to be in danger. Some skunks can go for months or even years without spraying musk. That's fine with them. Skunks want to avoid trouble, and "play fair" with their many warnings. A skunks’s stripes point to where the spray comes out. A 2011 study found that animal species that choose fight over flight when faced with a predator often have markings that draw attention to their best weapon. So while a badger has stripes on his face to highlight his sharp teeth, skunks’ stripes are perfectly positioned to highlight their ability to spray potential threats. By http://www.birdphotos.com via Wikimedia Commons Skunks are so nice that some people want to keep them as pets. The striped skunk is the most social skunk and the one most commonly domesticated. The legality of keeping skunks as pets in the US varies by state, with it being illegal in a majority of them. By Matt MacGillivray via Wikimedia Commons  Larry Pringle has written many animal books, among them The Secret Life of the Red Fox. His The Secret Life of the Skunk was published by Boyds Mills Press in 2019. It is about spring and summer in the lives of a mother striped skunk and her kits. ML 8 Citation
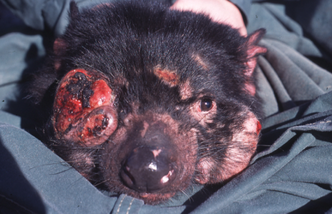
Pringle, Laurence. "How Skunks Play Fair." Nonfiction Minute, iNK Think Tank, 8 Nov. 2017, www.nonfictionminute.org/how-skinks-play-fair.  Lots of people are fond of the cartoon character called Taz. He is loud, always hungry, not very smart, and sometimes spins his body around like a little tornado. He pops up in video games and even appears in television ads. Cartoon Taz is based on a real animal known as a Tasmanian devil. The “devils” are marsupials related to kangaroos and wombats. They used to live in Australia, but now survive only on Tasmania, an island state just south of the Australian mainland. Tasmanian devils have black fur, short legs, and are about the size of a beagle dog or a big house cat. Long ago, people named them "devils" because of their sounds. They grunt, huff, snarl, and click their teeth but especially give out loud, fierce, blood-curdling screeches and screams. And you know that spinning tornado thing that cartoon Taz does? It is based on the animal's actual behavior. When a Tasmanian devil is in a fight, or defending itself, it moves very rapidly. It flashes a view of its side, making itself look as big as possible. Then it quickly shows its front, with gaping mouth and teeth. Back and forth, back and forth it turns, showing two kinds of threats, and appearing to be whirling around. Tasmanian devils fight a lot. They battle over food, and in mating season, males compete for females. This behavior has helped put their whole species in big trouble. Beginning in 1996, a disease began to kill the devils. It's a cancer that grows quickly on the faces of these mammals. When they fight, they often bite one another's face. This spreads the disease. An infected animal soon dies. In less than 20 years the whole Tasmanian devil population dropped by ninety percent. Still, there is hope. Scientists have learned more about the disease, and perhaps a vaccine can be created to protect devils. Also, healthy devils are being kept in zoos and other places where the disease can't reach them. And scientists have learned that some wild devils in Tasmania seem able to resist the disease. With help from people, Tasmanian devils may survive. We can hope these fascinating creatures make a comeback, and once again scream loudly in the Tasmanian night.
 We have been taught to fear scorpions in any form. But scorpions usually sting either to subdue their prey or to protect themselves. In fact, Earth has two thousand scorpion species, but only a few dozen are deadly to humans. With vivid descriptions of scorpions’ life cycle, body structure, habits, and habitat and beautiful, realistic illustrations, Laurence Pringle's Scorpions! Strange and Wonderful explores one of nature’s feared and misunderstood creatures. For more information, click here. MLA 8 Citation
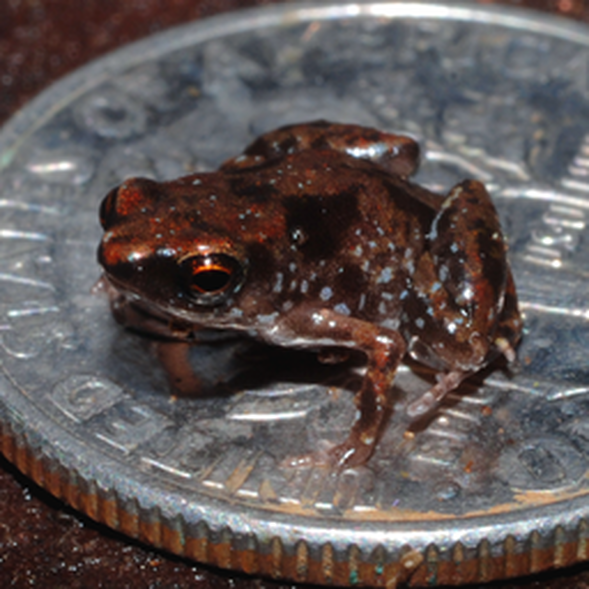
Pringle, Laurence. "Taz in Big Trouble." Nonfiction Minute, iNK Think Tank, 9 Feb. 2018, www.nonfictionminute.org/the-nonfiction-minute/ taz-in-big-trouble. Can you name the world's fastest mammal? How about the biggest shark? If you said the cheetah, and the whale shark, you’re right! It's safe to say that we will probably never discover faster, or bigger, animals. However, it is still possible to find small animals that can set new records for being tiny. Take frogs, for example. For many years, two kinds of frogs were tied for the honor of being the world's smallest. One species lives in Cuba, the other in Brazil. These frogs are so small that one can perch its whole body on a United States dime. Look at a dime and imagine an adult frog sitting there! Recently, those two little species from Cuba and Brazil lost their title as Earth's smallest frogs, thanks to two scientists from the United States. They were herpetologists (scientists who study amphibians, including salamanders and frogs). In 2009 these scientists were studying frog calls on Papua New Guinea a large island nation north of Australia, in the Pacific Ocean. The scientists were recording frog calls at night. All around, they heard chirping sounds that came from dead leaves on the forest floor. "Probably insects," they thought, but they decided to check. They searched among the leaves but found nothing. Frustrated, they grabbed whole handfuls of leaves and stuffed them into a clear plastic bag. Then they slowly searched through the bag, leaf by leaf. A small frog hopped off one of the leaves! When I say "small frog," I mean one that can sit on a dime with room to spare. It was just 7.7 millimeters long. That's less than a third of an inch. Though the scientists later discovered another slightly bigger relative, the first one is now officially Earth's smallest frog—and Earth's smallest four-footed animal. These tiny frogs are hard to catch. They can leap 30 times their own length. But the herpetologists managed to catch quite a few, take photos of them, and learn about their lives, close up. It wasn't until January 2012 that the scientists announced their discovery. Since this frog was discovered near a village called Amau, it was given the scientific name of Amauensis. Eventually, people may come to call it the Amau frog. In the world of science, the tiny Amau frogs are very big news.  The tiny Amau frogs were discovered just before Laurence Pringle's book on frogs was published--too late to include this big news. At the end of his book FROGS!, Larry has an Author’s Note called “A Life Full of Frogs” in which he tells about his close encounters with frogs as a child, as a father, as a wildlife photographer, and as a neighborhood ecologist acting locally to protect and even create anuran habitats. His relationship with frogs continues to this day. He says, "Our Spring evenings are sweetened by a chorus of spring peepers from the neighborhood wetland forest. Also, almost every day we visit our backyard garden pond. Several green frogs, large and small, live there. There are tadpoles of both green frogs and gray tree frogs." Pringle, Laurence. "Tiny Frogs Are Big News." Nonfiction Minute, iNK Think Tank, 13 Oct. 2017, www.nonfictionminute.org/the-nonfiction-minute/tiny-frogs-are-big-news. |
*NEWS
|
For Vicki Cobb's BLOG (nonfiction book reviews, info on education, more), click here: Vicki's Blog
The NCSS-CBC Notable Social Studies Committee is pleased to inform you
that 30 People Who Changed the World has been selected for Notable Social Studies Trade Books for Young People 2018, a cooperative project of the National Council for the Social Studies (NCSS) & the Children’s Book Council
Categories
All
Abolitionists
Adams Janus
Adaptation
Adaptations
Adkins Jan
Advertising
Aerodynamics
Africa
African American History
African Americans
Africa West
Agriculture
Aircraft
Air Pilots
Air Pressure
Air Travel
Albee Sarah
Alchemy
Alligators
Allusion
American History
American Icons
Amphibians
Amundsen Roald
Anatomy
Ancient
Ancient Cultures
Anderson Marian 1897-1993
Animal Behavior
Animal Experimentation
Animal Intelligence
Animals
Animation
Antarctica
Ants
Apache Indians
Apes
April Fool's Day
Architecture
Argument
Arithmetic
Art
Art Deco
Artists
Arts
Asia
Astronauts
Astronomy
Athletes
Atomic Theory
Audubon Societies
Authors
Autobiography
Automobiles
Aviation
Awards
Bacteria
Baseball
Battuta Ibn
Bears
Beatles
Beavers
Bees
Biodegradation
Biography
Biology
Biomes
Biomimicry
Biplanes
Birds
Black Death
Black History
Blindness
Blizzards
Bombs
Bonaparte Napoleon
Boone Daniel
Botany
Brazil
Bridges
Brill Marlene Targ
Brooklyn Bridge
Brown John
Buffaloes
Building Materials
Butterflies
Caesar
Caesar Julius
Caissons
Calculus
Calendars
Cannibal
Capitals
Caravaggio
Carbon Dioxide
Carnivores
Carson Mary Kay
Cartoons & Comics
Carving (Decorative Arts)
Cascade Range
Castaldo Nancy
Castles
Castrovilla Selene
Cathedrals
Cats
Caves
Celts
Cemeteries
Chemistry
Children's Authors
Child Welfare
China
Choctaw Indians
Christmas
Chronometers
Cicadas
Cinco De Mayo
Ciphers
Circle
Citizenship
Civil Rights
Civil Rights Movements
Civil War
Civil War - US
Climate
Climate Change
Clocks And Watches
Clouds
Cobb Vicki
COBOL (Computer Language)
Code And Cipher Stories
Collard III Sneed B.
Collectors And Collecting
Color
Commerce
Communication
Competition
Compilers
Composers
Computers
Congressional Gold Medal
Consitution
Contests
Contraltos
Coolidge Calvin
Cooling
Corms
Corn
Counterfeiters
Covid-19
Crocodiles
Cryptography
Culture
Darwin Charles
Declaration Of Independence
Decomposition
Decompression Sickness
Deep-sea Animals
Deer
De Medici Catherine
Design
Detectives
Dickens Charles
Disasters
Discrimination
Diseases
Disney Walt
DNA
Dogs
Dollar
Dolphins
Douglass Frederick 1818-1895
Droughts
Dr. Suess
Dunphy Madeleine
Ear
Earth
Earthquakes
Ecology
Economics
Ecosystem
Edison Thomas A
Education
Egypt
Eiffel-gustave-18321923
Eiffel-tower
Einstein-albert
Elephants
Elk
Emancipationproclamation
Endangered Species
Endangered-species
Energy
Engineering
England
Englishlanguage-arts
Entomology
Environmental-protection
Environmental-science
Equinox
Erie-canal
Etymology
Europe
European-history
Evolution
Experiments
Explorers
Explosions
Exports
Extinction
Extinction-biology
Eye
Fairs
Fawkes-guy
Federalgovernment
Film
Fires
Fishes
Flight
Floods
Flowers
Flute
Food
Food-chains
Foodpreservation
Foodsupply
Food-supply
Football
Forceandenergy
Force-and-energy
Forensicscienceandmedicine
Forensic Science And Medicine
Fossils
Foundlings
France
Francoprussian-war
Freedom
Freedomofspeech
French-revolution
Friction
Frogs
Frontier
Frontier-and-pioneer-life
Frozenfoods
Fugitiveslaves
Fultonrobert
Galapagos-islands
Galleys
Gametheory
Gaudi-antoni-18521926
Gender
Generals
Genes
Genetics
Geography
Geology
Geometry
Geysers
Ghosts
Giraffe
Glaciers
Glaucoma
Gliders-aeronautics
Global-warming
Gods-goddesses
Gold-mines-and-mining
Government
Grant-ulysses-s
Grasshoppers
Gravity
Great-britain
Great-depression
Greece
Greek-letters
Greenberg Jan
Hair
Halloween
Handel-george-frederic
Harness Cheryl
Harrison-john-16931776
Health-wellness
Hearing
Hearing-aids
Hearst-william-randolph
Henry-iv-king-of-england
Herbivores
Hip Hop
History
History-19th-century
History-france
History-world
Hitler-adolph
Hoaxes
Holidays
Hollihan Kerrie Logan
Homestead-law
Hopper-grace
Horses
Hot Air Balloons
Hot-air-balloons
Housing
Huguenots
Human Body
Hurricanes
Ice
Icebergs
Illustration
Imagery
Imhotep
Imperialism
Indian-code-talkers
Indonesia
Industrialization
Industrial-revolution
Inquisition
Insects
Insulation
Intelligence
Interstatecommerce
Interviewing
Inventions
Inventors
Irrational-numbers
Irrigation
Islands
Jacksonandrew
Jazz
Jeffersonthomas
Jefferson-thomas
Jemisonmae
Jenkins-steve
Jet-stream
Johnsonlyndonb
Jokes
Journalism
Keeling-charles-d
Kennedyjohnf
Kenya
Kidnapping
Kingmartinlutherjr19291968
Kingmartinlutherjr19291968d6528702d6
Kings-and-rulers
Kings Queens
Kings-queens
Koala
Labor
Labor Policy
Lafayette Marie Joseph Paul Yves Roch Gilbert Du Motier Marquis De 17571834
Landscapes
Languages-and-culture
Law-enforcement
Layfayette
Levers
Levinson Cynthia
Lewis And Clark Expedition (1804-1806)
Lewis Edmonia
Liberty
Lift (Aerodynamics)
Light
Lindbergh Charles
Liszt Franz
Literary Devices
Literature
Lizards
Longitude
Louis XIV King Of France
Lumber
Lunar Calendar
Lynching
Macaws
Madison-dolley
Madison-james
Madison-james
Mammals
Maneta-norman
Maneta-norman
Marathon-greece
Marine-biology
Marine-biology
Marines
Marsupials
Martial-arts
Marx-trish
Mass
Massachusetts-maritime-academy
Mass-media
Mastodons
Mathematics
May-day
Mcclafferty-carla-killough
Mcclafferty-carla-killough
Mckinley-william
Measurement
Mechanics
Media-literacy
Media-literacy
Medicine
Memoir
Memorial-day
Metaphor
Meteorology
Mexico
Mickey-mouse
Microscopy
Middle-west
Migration
Military
Miners
Mississippi
Molasses
Monarchy
Monsters
Montgomery
Montgomery-bus-boycott-19551956
Montgomery-heather-l
Monuments
Moon
Moran-thomas
Morsecode
Morsesamuel
Moss-marissa
Moss-marissa
Motion
Motion-pictures
Mummies
Munro-roxie
Munro-roxie
Musclestrength
Museums
Music
Muslims
Mythologygreek
Nanofibers
Nanotechnology
Nathan-amy
Nathan-amy
Nationalfootballleague
Nationalparksandreserves
Nativeamericans
Native-americans
Native-americans
Naturalhistory
Naturalists
Nature
Nauticalcharts
Nauticalinstruments
Navajoindians
Navigation
Navy
Ncaafootball
Nervoussystem
Newdeal19331939
Newman-aline
Newman-aline
Newton-isaac
New-york-city
Nobelprizewinners
Nomads
Nonfictionnarrative
Nutrition
Nylon
Nymphs-insects
Oaths Of Office
Occupations
Ocean
Ocean-liners
Olympics
Omnivores
Optics
Origami
Origin
Orphans
Ottomanempire
Painters
Painting
Paleontology
Pandemic
Paper-airplanes
Parksrosa19132005
Parrots
Passiveresistance
Patent Dorothy Hinshaw
Peerreview
Penguins
Persistence
Personalnarrative
Personification
Pets
Photography
Physics
Pi
Pigeons
Pilots
Pinkertonallan
Pirates
Plague
Plains
Plainsindians
Planets
Plantbreeding
Plants
Plastics
Poaching
Poetry
Poisons
Poland
Police
Political-parties
Pollen
Pollution
Polo-marco
Populism
Portraits
Predation
Predators
Presidentialmedaloffreedom
Presidents
Prey
Prey-predators
Prey-predators
Prime-meridian
Pringle Laurence
Prohibition
Proteins
Protestandsocialmovements
Protestants
Protestsongs
Punishment
Pyramids
Questioning
Radio
Railroad
Rainforests
Rappaport-doreen
Ratio
Reading
Realism
Recipes
Recycling
Refrigerators
Reich-susanna
Religion
Renaissance
Reproduction
Reptiles
Reservoirs
Rheumatoidarthritis
Rhythm-and-blues-music
Rice
Rivers
Roaringtwenties
Roosevelteleanor
Rooseveltfranklind
Roosevelt-franklin-d
Roosevelt-theodore
Running
Russia
Safety
Sanitation
Schwartz David M
Science
Scientificmethod
Scientists
Scottrobert
Sculpture
Sculpturegardens
Sea-level
Seals
Seals-animals
Secretariesofstate
Secretservice
Seeds
Segregation
Segregationineducation
Sensessensation
September11terroristattacks2001
Seuss
Sextant
Shackletonernest
Shawneeindians
Ships
Shortstories
Silkworms
Simple-machines
Singers
Siy Alexandra
Slavery
Smuggling
Snakes
Socialchange
Social-change
Socialjustice
Social-justice
Socialstudies
Social-studies
Social-studies
Sodhouses
Solarsystem
Sound
Southeast-asia
Soybean
Space Travelers
Spain
Speech
Speed
Spiders
Spies
Spiritualssongs
Sports
Sports-history
Sports-science
Spring
Squirrels
Statue-of-liberty
STEM
Storms
Strategy
Sugar
Sumatra
Summer
Superbowl
Surgery
Survival
Swanson-jennifer
Swinburne Stephen R.
Synthetic-drugs
Taiwan
Tardigrada
Tasmania
Tasmanian Devil
Tasmanian-devil
Technology
Tecumsehshawneechief
Telegraph-wireless
Temperature
Tennis
Terrorism
Thomas Peggy
Thompson Laurie Ann
Time
Titanic
Tombs
Tortoises
Towle Sarah
Transcontinental-flights
Transportation
Travel
Trees
Trung Sisters Rebellion
Tundra
Turnips
Turtles
Typhoons
Underground Railroad
Us-environmental-protection-agency
Us History
Us-history
Ushistoryrevolution
Us History Revolution
Us-history-war-of-1812
Us Presidents
Ussupremecourtlandmarkcases
Vacations
Vaccines
Vangoghvincent
Vegetables
Venom
Vietnam
Viruses
Visual-literacy
Volcanoes
Voting-rghts
War
Warne-kate
Warren Andrea
Washington-dc
Washington George
Water
Water-currents
Wax-figures
Weapons
Weather
Weatherford Carole Boston
Whiting Jim
Wildfires
Winds
Windsor-castle
Wolves
Woman In History
Women
Women Airforce Service Pilots
Women-airforce-service-pilots
Womeninhistory
Women In History
Women-in-science
Women's History
Womens-roles-through-history
Wonder
Woodson-carter-godwin-18751950
World-war-i
World War Ii
World-war-ii
Wright Brothers
Writing
Writing-skills
Wwi
Xrays
Yellowstone-national-park
Zaunders Bo
ArchivesMarch 2021
February 2021
January 2021
December 2020
November 2020
October 2020
September 2020
June 2020
May 2020
April 2020
March 2020
February 2020
January 2020
December 2019
October 2019
September 2019
August 2019
July 2019
May 2019
April 2019
March 2019
February 2019
January 2019
December 2018
November 2018
September 2018
June 2018
May 2018
April 2018
March 2018
February 2018
January 2018
December 2017
November 2017
October 2017
September 2017
March 2017
The NONFICTION MINUTE, Authors on Call, and. the iNK Books & Media Store are divisions of iNK THINK TANK INC.
a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit corporation. To return to the iNK Think Tank landing page click the icon or the link below. :
http://inkthinktank.org/
For more information or support, contact thoughts@inkthinktank.org
For Privacy Policy, go to
Privacy Policy
© COPYRIGHT the Nonfiction Minute 2020.
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
This site uses cookies to personalize your experience, analyze site usage, and offer tailored promotions. www.youronlinechoices.eu
Remind me later
Archives
March 2023
February 2023
January 2023
December 2022
November 2022
October 2022
September 2022
June 2022
May 2022
April 2022
March 2022
February 2022
January 2022
December 2021
November 2021
September 2021
April 2021
March 2021
February 2021
November 2020
October 2020
September 2020
June 2020
May 2020
April 2020
March 2020
February 2020
January 2020
October 2019
August 2019
July 2019
May 2019
April 2019
December 2018
September 2018
June 2018
May 2018
March 2018
February 2018
January 2018
December 2017
November 2017
October 2017
September 2017























 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
