
 The Earth Day Flag created by John McConnell The Earth Day Flag created by John McConnell
The celebrated astrophysicist, Neil deGrasse Tyson, said, “People never look up.” Tyson or Starman, as he is called, is right. Look up and you’ll see amazing stuff: puffy cumulonimbus clouds rising 60,000 feet, broken rainbows, blue skies bluer than blue, Venus and Mars huddling beside the new moon, the Milky Way.
When you look up, you can’t help realize you are standing, feet firmly planted, on planet Earth. We are attached in a very physical way to this place...this planet called Earth. So, not only look up, but, as Rachel Carson declared in many of her writings, “Look around, and down, and closer.” Whether you are looking up or looking down, we celebrate our home planet every year on April 22. This celebration or “birthday” is called Earth Day and it has been going on since 1970 after Gaylord Nelson, a U.S. Senator from Wisconsin, proposed a day of national focus on environmental issues. Buoyed by the success of Rachel Carson’s book Silent Spring, about the concern for living organisms and the environment, Earth Day 1970 set out to raise public awareness for the health and harmony of the planet. People from all walks of life— young and old, farmers and urban dwellers, liberals and conservatives— banded together and achieved great things. The first Earth Day on April 22, 1970 led to the creation of the United States Environmental Protection Agency and the passage of the Clean Air Act, the Clean Water Act, and the Endangered Species Act. And now, forty-six years later, Earth Day 2016 has gone truly global. Around the world, people celebrate Earth Day with massive rallies, marches and festivals. But for many people it is not just an annual event, but all the quiet acts and the simple habits performed throughout the year. For instance, I make it a habit of recycling every piece of plastic I use (or as much as humanly possible). Less plastic that ends up in the oceans means happier and healthier sea turtles and whales. If you want some ideas about how you can demonstrate your support for environmental protection, you might start by checking out the book, Recycle This Book - 100 Top Children’s Book Authors Tell You How To Go Green. And if you link to the Earth Day website, you can take a peek at all the great activities planned around the world on April 22, 2018. Let’s make this the best Earth Day ever...all year long! 
With essays from renowned children’s book authors such as Ann Brashares, Jeanne DuPrau, Caroline B. Cooney, Laurie Halse Anderson, Bruce Coville, Gennifer Choldenko, and more than 100 others, each piece is an informative and inspiring call to kids of all ages to understand what’s happening to the environment, and to take action in saving our world. Helpful tips and facts are interspersed throughout.

Part of the award-winning Scientists in the Field book series, Sea Turtle Scientist introduces Dr. Kimberly Stewart, “the turtle lady,” and describes her work on St. Kitts with endangered loggerhead sea turtles. The book provides extensive information on sea turtles and Dr. Stewart’s research, as well as the efforts of WIDECAST to preserve and protect these amazing creatures. For more information, visit the author's website.
Stephen R. Swinburne is a member of iNK's Authors on Call and is available for classroom programs through Field Trip Zoom, a terrific technology that requires only a computer, wifi, and a webcam. Click here to find out more.
MLA 8 Citation
0 Comments
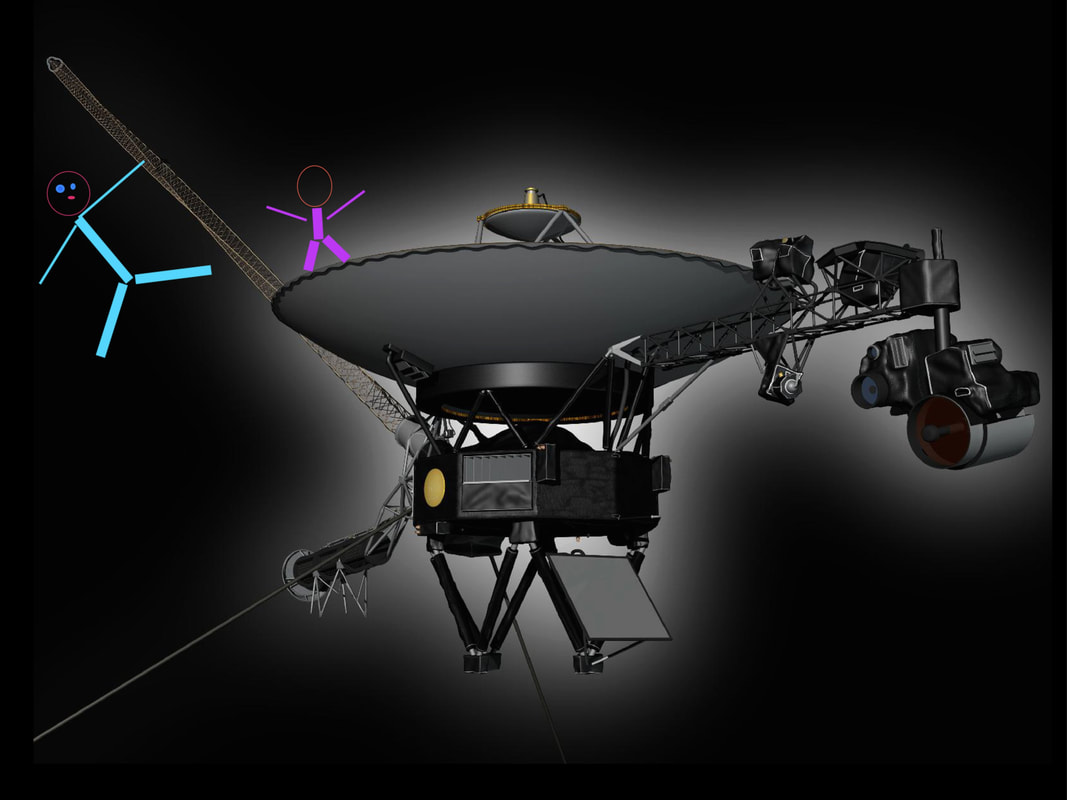
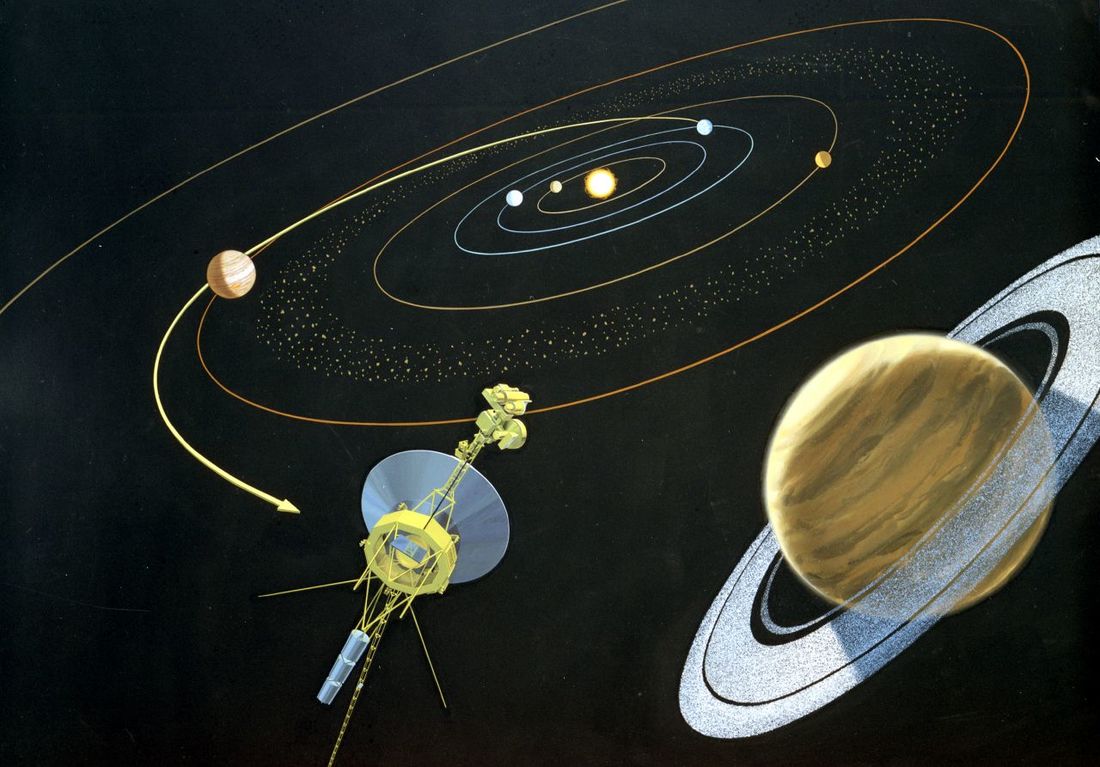
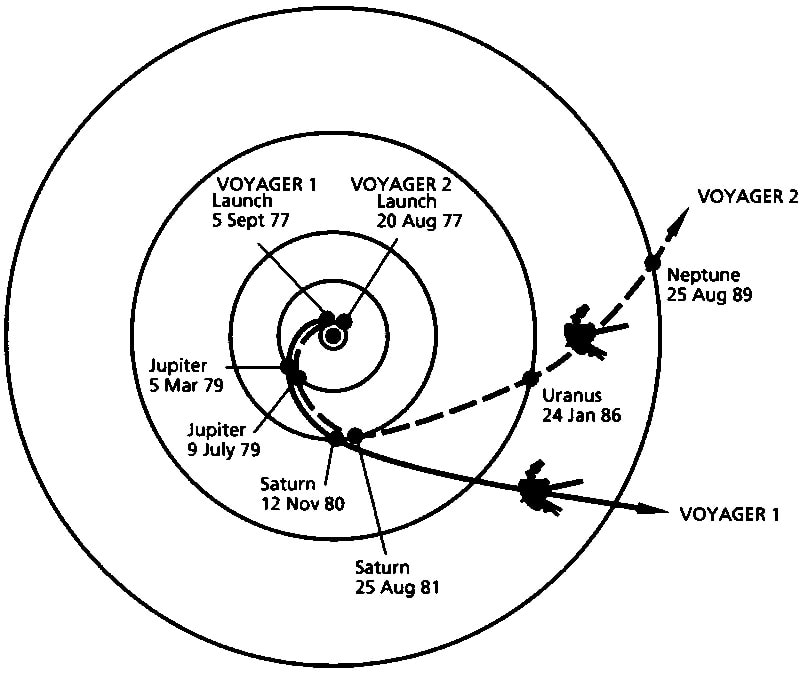
 A light year is not a year that has gone on a diet. It is not a year that’s been trimmed to 300 days. It’s not a year spent under high-wattage lamps. A light year isn’t any kind of year. A light year is a distance. It is a vast distance; the distance light travels in a year. To appreciate a light year, you have to understand how fast light travels. The speed of light is truly mind-boggling: 186,000 miles per . . . second. That’s “per second,” not “per hour.” In one tick-tock second, light travels a distance of 186,000 miles. If it could go in circles, it could travel around the earth more than seven times in just one second! But light travels in straight lines, not in circles. Imagine something traveling that fast in a straight line—not for a second, not for a minute, not for an hour, not for a day, but for an entire year. The distance it goes in that year is called a light year. A light year is a convenient unit of measure when distances are enormous. You could talk about the same distances in miles. It's about 5,878,499,810,000 (5 trillion, 878 billion, 499 million, 810 thousand ) of them. But these measurements are so large that they are unwieldy. It's much easier to just name that enormous distance with two simple words: a "light year." The star closest to our solar system is Proxima Centauri. Some of the light that leaves Proxima Centauri goes to Earth, cruising along at 186,000 miles per second. At that speed, light takes about 4.2 years to get to Earth from Proxima Centauri So how far away is Proxima Centauri? It is 4.2 light years away. To give you an idea of how far that is, imagine going to Proxima Centauri in a spaceship traveling at the speed of the space shuttle — about ten miles per second. (That’s much faster than airplanes can fly.) You would get there in about 70,000 years. Our Sun is much closer than Proxima Centauri. It is 93 million miles away. There is another way to refer to the distance from the earth to the Sun. Light leaving the Sun takes about eight minutes to get to Earth, so we say the Sun is eight “light minutes” away. If you traveled at the speed of light, you could get there in eight minutes. Have a nice trip! © David M. Schwartz, 2014  David Schwartz has been fascinated by big numbers and big distances ever since he was a little boy riding his bicycle, wondering “How long would it take for me to ride to Proxima Centauri, 4.2 light years away?” He wrote about light years in his math alphabet book G Is for Googol. David is a member of iNK’s Authors on Call. He can visit in your classroom via interactive video conferencing. Learn more here. MLA 8 Citation Schwartz, David M. "What Is a Light Year?" Nonfiction Minute, iNK Think Tank, 14 Sept. 2017, www.nonfictionminute.org/the-nonfiction-minute/what-is-a-light-year. Do you ever feel spaced-out before you take a test? Yes or no, let’s go! 1. TRUE or FALSE? It’s possible for a spacecraft to fly from Earth to Venus, to Mars, back to Earth, then to Saturn, out to Pluto, back to Jupiter, and come home to Earth on one tank of fuel. 2. It’s possible for a spacecraft to fly all over the solar system on one tank of fuel because of: a. the sling-shot effect b. gravity assist c. swing-by d. all of the above e. none of the above The sling-shot effect, also known as a swing-by or gravity assist, is used to accelerate a spacecraft. Acceleration means to change the speed and/or the direction of a moving body. A spacecraft that is speeding up, slowing down, or following a curved path is accelerating. Gravity accelerates objects everywhere in the Universe. When you ride your bike up a hill it takes a lot of effort to make it to the top because the Earth is massive compared to you, and gravity pulls you toward its center. When you coast down the other side, gravity is your friend! Spacecraft can use the gravity of a planet to accelerate. Picture a spacecraft falling toward a planet. The spacecraft will crash unless it steers away. 3. As a spacecraft accelerates toward a planet, the motion of the planet is also affected by the gravity exerted by: a. the spacecraft b. the Sun c. cosmic rays d. both (a) and (b) e. both (b) and (c) f. all of the above g. none of the above All bodies in space, no matter how big or small, exert gravity on each other. Planets stay in orbit around the sun because of gravity. A planet is also affected by the tiny mass of a spacecraft. Gravity assist was used to increase the speed of Voyager 1 by 36,000 mph on its swing by Jupiter, which sling shot it to Saturn. And Jupiter slowed down infinitesimally, at a rate of 12 inches per one trillion years. 4. The person who discovered the math for using gravity assist to accelerate a spacecraft from planet to planet to planet…was: a. Aristotle (384 B.C. to 322 B.C) b. Galileo (1564-1642) c. Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) d. Katherine Johnson (1918- ) e. Michael Minovitch (1936- ) END OF TEST! DON’T STOP WORKING. START TALKING. ASK QUESTIONS. GO TO THE LIBRARY TO FIND THE ANSWERS. In this drawing a spacecraft gets an assist from Jupiter as it "slingshots" toward Saturn. Image courtesy of NASA/JPL Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 used gravity assist to fly by the outer planets. Image courtesy of NASA The twin Voyagers have no people on board on their interstellar journey, but carry The Golden Record, which contains messages, music, and pictures from Earth. Image courtesy of NASA/Alexandra Siy In case you didn't make it to the library: In 1961, UCLA graduate student Michael Minovitch used math and the new IBM 7090-7094 computers to invent gravity assist trajectories for space flight. Used with permission of Michael Minovitch  Alexandra Siy's Voyager's Greatest Hits tells the story of the twin space probes that traveled to Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, a journey beyond our solar system into interstellar space, where no probe has ventured before. Siy tells the fascinating story of how the Voyager probes work, where the probes have been and what they’ve seen, and what they carry on board. Alexandra Siy is also a member of Authors on Call. You can bring her to your classroom via interactive videoconferencing and learn more from her and ask her questions. To find out more go here. MLA 8 Citation
Siy, Alexandra. "Spaced Out." Nonfiction Minute, iNK Think Tank, 2 May 2018, www.nonfictionminute.org/the-nonfiction-minute/Spaced-Out.  When musicians play a lively tune, they often find themselves spontaneously tapping their toes and moving about to the pulsing beat. But when Ellen Ochoa played her flute at work one day in 1993, she couldn’t be spontaneous at all. If she hadn’t made careful plans, she could have been blown about the room, just by playing one long note on her flute. That’s because she was an astronaut working on the U.S. Space Shuttle as it circled Earth more than a hundred miles out in space. Gravity is so weak far out in space that astronauts—and any of their gear that isn’t fastened down—will float about inside a space craft. Blowing air into her flute could have created enough force to actually send Ochoa zipping about the space shuttle cabin. So, to keep herself in place as she played, she had to slip her feet into strong loops attached to the floor. Dr. Ochoa, now the director of NASA’s Johnson Space Center, was the first U.S. astronaut to bring a flute on a space mission, but she wasn’t the first to make music in space. Nearly thirty years earlier, in December 1965, two astronauts onboard the Gemini 6 space craft played a musical joke on mission control officials down on Earth. Those astronauts—Walter M. Schirra, Jr., and Thomas P. Stafford—told mission control that they saw an unusual object near their spaceship, a satellite perhaps, moving from North to South. They said they would try to pick up some sound from this mysterious object. Then they used the harmonica and bells they had secretly brought with them on that December mission to surprise folks listening down below by playing “Jingle Bells.” In recent years, other astronauts have brought musical instruments on space missions to help lift their spirits, especially those who spend many months on the International Space Station. Like Dr. Ochoa, these astronaut musicians have to make adjustments, such as using a bungee cord to attach an electronic piano keyboard to a pianist’s leg. Some astronauts have composed music in space, including Canadian Chris Hadfield. On May 6, 2013, he sang the song he wrote—called “I.S.S. (Is Somebody Singing)”—in a live TV broadcast from the space station as thousands of Canadian schoolchildren sang along with him down on Earth. Click here for a recording of that space-to-Earth performance  Learning to play an instrument can be fun and, at times, frustrating. Amy Nathan's lively book helps young people cope with the difficulties involved in learning a new instrument and remaining dedicated to playing and practicing. Teens from renowned music programs - including the Juilliard School's Pre-College Program and Boston University's Tanglewood Institute - join pro musicians in offering practical answers to questions from what instrument to play to where the musical road may lead. For more information, click here. MLA 8 Citation
Nathan, Amy. "Music That's Out of This World." Nonfiction Minute, iNK Think Tank, 11 May 2018, www.nonfictionminute.org/the-nonfiction-minute/ Music-Thats-Out-of-This-World.  Imagine Earth as a button. I don’t mean you’re going to sew it onto your shirt. But imagine the planet Earth shrunk to the size of a button. (Of course Earth is not flat like a button but we’re giving our shrunken Earth the same diameter as a shirt button.) Go ahead and draw a circle around a shirt button. Call it “Earth.” Suppose you wanted to draw Jupiter, the largest planet, at the same scale as this micro-Earth. That means you’re going to shrink it to the same fraction of its original size as our button-Earth. What size would little Jupiter be? One way to find out would be to calculate how many times bigger the real Jupiter is than the real Earth. Earth’s diameter is about 8,000 miles (13,000 kilometers). Jupiter’s is about 88,000 miles (143,000 km). Divide the size of Jupiter by the size of Earth to see that Jupiter is about 11 times bigger. So, since Jupiter’s diameter is 11 times that of Earth’s, put 11 buttons in a line to show the diameter of Jupiter. Then draw the circle that represents Jupiter. If you don’t have 11 buttons, just look at the picture. Did you think the Earth was a big place? Look at it compared with Jupiter! But what about the sun? The sun’s diameter is about 865,000 miles (1,400,000 km). That means it’s almost 10 times bigger than Jupiter. Can you find a way to draw a circle 10 times the size of our Jupiter? We’ve drawn part of it for you, on the same scale as our button-sized Earth. On the picture, it’s labeled “our arc.” (An arc is part of a circle.) Looking at the arc, you can imagine the rest of the circle and compare the sun to Jupiter and Earth. A minute ago, you thought Jupiter was big. Now it looks shrimpy compared to the sun! But is the sun really gigantic? Do some research to find out the size of a red giant star like the strangely named Betelguese (pronounced “beetle-juice.”) Figure out what it looks like compared to our sun, which is a medium-sized star. You may be amazed at the difference. And you thought the sun was big! Is anything truly big? Is anything truly small? Or does that depend on what it’s being compared to?  If the Earth were the size of a button, Jupiter’s diameter would equal eleven buttons because the diameter of Jupiter is eleven times that of Earth. If the Earth were the size of a button, Jupiter’s diameter would equal eleven buttons because the diameter of Jupiter is eleven times that of Earth. Both images are by Marissa Moss, the illustrator of David M Schwartz's book, G is for Googol.  G is for Googol: A Math Alphabet Book is a wonder-filled romp through the world of mathematics. For more information, click here. David Schwartz is a member of iNK's Authors on Call and is available for classroom programs through Field Trip Zoom, a terrific technology that requires only a computer, wifi, and a webcam. Click here to find out more. MLA Citation
Schwartz, David M. "If the Earth Were a Button." Nonfiction Minute, iNK Think Tank, 16 Jan. 2018, www.nonfictionminute.org/the-nonfiction-minute/ If-the-Earth-Were-a-Button. |
*NEWS
|
For Vicki Cobb's BLOG (nonfiction book reviews, info on education, more), click here: Vicki's Blog
The NCSS-CBC Notable Social Studies Committee is pleased to inform you
that 30 People Who Changed the World has been selected for Notable Social Studies Trade Books for Young People 2018, a cooperative project of the National Council for the Social Studies (NCSS) & the Children’s Book Council
Categories
All
Abolitionists
Adams Janus
Adaptation
Adaptations
Adkins Jan
Advertising
Aerodynamics
Africa
African American History
African Americans
Africa West
Agriculture
Aircraft
Air Pilots
Air Pressure
Air Travel
Albee Sarah
Alchemy
Alligators
Allusion
American History
American Icons
Amphibians
Amundsen Roald
Anatomy
Ancient
Ancient Cultures
Anderson Marian 1897-1993
Animal Behavior
Animal Experimentation
Animal Intelligence
Animals
Animation
Antarctica
Ants
Apache Indians
Apes
April Fool's Day
Architecture
Argument
Arithmetic
Art
Art Deco
Artists
Arts
Asia
Astronauts
Astronomy
Athletes
Atomic Theory
Audubon Societies
Authors
Autobiography
Automobiles
Aviation
Awards
Bacteria
Baseball
Battuta Ibn
Bears
Beatles
Beavers
Bees
Biodegradation
Biography
Biology
Biomes
Biomimicry
Biplanes
Birds
Black Death
Black History
Blindness
Blizzards
Bombs
Bonaparte Napoleon
Boone Daniel
Botany
Brazil
Bridges
Brill Marlene Targ
Brooklyn Bridge
Brown John
Buffaloes
Building Materials
Butterflies
Caesar
Caesar Julius
Caissons
Calculus
Calendars
Cannibal
Capitals
Caravaggio
Carbon Dioxide
Carnivores
Carson Mary Kay
Cartoons & Comics
Carving (Decorative Arts)
Cascade Range
Castaldo Nancy
Castles
Castrovilla Selene
Cathedrals
Cats
Caves
Celts
Cemeteries
Chemistry
Children's Authors
Child Welfare
China
Choctaw Indians
Christmas
Chronometers
Cicadas
Cinco De Mayo
Ciphers
Circle
Citizenship
Civil Rights
Civil Rights Movements
Civil War
Civil War - US
Climate
Climate Change
Clocks And Watches
Clouds
Cobb Vicki
COBOL (Computer Language)
Code And Cipher Stories
Collard III Sneed B.
Collectors And Collecting
Color
Commerce
Communication
Competition
Compilers
Composers
Computers
Congressional Gold Medal
Consitution
Contests
Contraltos
Coolidge Calvin
Cooling
Corms
Corn
Counterfeiters
Covid-19
Crocodiles
Cryptography
Culture
Darwin Charles
Declaration Of Independence
Decomposition
Decompression Sickness
Deep-sea Animals
Deer
De Medici Catherine
Design
Detectives
Dickens Charles
Disasters
Discrimination
Diseases
Disney Walt
DNA
Dogs
Dollar
Dolphins
Douglass Frederick 1818-1895
Droughts
Dr. Suess
Dunphy Madeleine
Ear
Earth
Earthquakes
Ecology
Economics
Ecosystem
Edison Thomas A
Education
Egypt
Eiffel-gustave-18321923
Eiffel-tower
Einstein-albert
Elephants
Elk
Emancipationproclamation
Endangered Species
Endangered-species
Energy
Engineering
England
Englishlanguage-arts
Entomology
Environmental-protection
Environmental-science
Equinox
Erie-canal
Etymology
Europe
European-history
Evolution
Experiments
Explorers
Explosions
Exports
Extinction
Extinction-biology
Eye
Fairs
Fawkes-guy
Federalgovernment
Film
Fires
Fishes
Flight
Floods
Flowers
Flute
Food
Food-chains
Foodpreservation
Foodsupply
Food-supply
Football
Forceandenergy
Force-and-energy
Forensicscienceandmedicine
Forensic Science And Medicine
Fossils
Foundlings
France
Francoprussian-war
Freedom
Freedomofspeech
French-revolution
Friction
Frogs
Frontier
Frontier-and-pioneer-life
Frozenfoods
Fugitiveslaves
Fultonrobert
Galapagos-islands
Galleys
Gametheory
Gaudi-antoni-18521926
Gender
Generals
Genes
Genetics
Geography
Geology
Geometry
Geysers
Ghosts
Giraffe
Glaciers
Glaucoma
Gliders-aeronautics
Global-warming
Gods-goddesses
Gold-mines-and-mining
Government
Grant-ulysses-s
Grasshoppers
Gravity
Great-britain
Great-depression
Greece
Greek-letters
Greenberg Jan
Hair
Halloween
Handel-george-frederic
Harness Cheryl
Harrison-john-16931776
Health-wellness
Hearing
Hearing-aids
Hearst-william-randolph
Henry-iv-king-of-england
Herbivores
Hip Hop
History
History-19th-century
History-france
History-world
Hitler-adolph
Hoaxes
Holidays
Hollihan Kerrie Logan
Homestead-law
Hopper-grace
Horses
Hot Air Balloons
Hot-air-balloons
Housing
Huguenots
Human Body
Hurricanes
Ice
Icebergs
Illustration
Imagery
Imhotep
Imperialism
Indian-code-talkers
Indonesia
Industrialization
Industrial-revolution
Inquisition
Insects
Insulation
Intelligence
Interstatecommerce
Interviewing
Inventions
Inventors
Irrational-numbers
Irrigation
Islands
Jacksonandrew
Jazz
Jeffersonthomas
Jefferson-thomas
Jemisonmae
Jenkins-steve
Jet-stream
Johnsonlyndonb
Jokes
Journalism
Keeling-charles-d
Kennedyjohnf
Kenya
Kidnapping
Kingmartinlutherjr19291968
Kingmartinlutherjr19291968d6528702d6
Kings-and-rulers
Kings Queens
Kings-queens
Koala
Labor
Labor Policy
Lafayette Marie Joseph Paul Yves Roch Gilbert Du Motier Marquis De 17571834
Landscapes
Languages-and-culture
Law-enforcement
Layfayette
Levers
Levinson Cynthia
Lewis And Clark Expedition (1804-1806)
Lewis Edmonia
Liberty
Lift (Aerodynamics)
Light
Lindbergh Charles
Liszt Franz
Literary Devices
Literature
Lizards
Longitude
Louis XIV King Of France
Lumber
Lunar Calendar
Lynching
Macaws
Madison-dolley
Madison-james
Madison-james
Mammals
Maneta-norman
Maneta-norman
Marathon-greece
Marine-biology
Marine-biology
Marines
Marsupials
Martial-arts
Marx-trish
Mass
Massachusetts-maritime-academy
Mass-media
Mastodons
Mathematics
May-day
Mcclafferty-carla-killough
Mcclafferty-carla-killough
Mckinley-william
Measurement
Mechanics
Media-literacy
Media-literacy
Medicine
Memoir
Memorial-day
Metaphor
Meteorology
Mexico
Mickey-mouse
Microscopy
Middle-west
Migration
Military
Miners
Mississippi
Molasses
Monarchy
Monsters
Montgomery
Montgomery-bus-boycott-19551956
Montgomery-heather-l
Monuments
Moon
Moran-thomas
Morsecode
Morsesamuel
Moss-marissa
Moss-marissa
Motion
Motion-pictures
Mummies
Munro-roxie
Munro-roxie
Musclestrength
Museums
Music
Muslims
Mythologygreek
Nanofibers
Nanotechnology
Nathan-amy
Nathan-amy
Nationalfootballleague
Nationalparksandreserves
Nativeamericans
Native-americans
Native-americans
Naturalhistory
Naturalists
Nature
Nauticalcharts
Nauticalinstruments
Navajoindians
Navigation
Navy
Ncaafootball
Nervoussystem
Newdeal19331939
Newman-aline
Newman-aline
Newton-isaac
New-york-city
Nobelprizewinners
Nomads
Nonfictionnarrative
Nutrition
Nylon
Nymphs-insects
Oaths Of Office
Occupations
Ocean
Ocean-liners
Olympics
Omnivores
Optics
Origami
Origin
Orphans
Ottomanempire
Painters
Painting
Paleontology
Pandemic
Paper-airplanes
Parksrosa19132005
Parrots
Passiveresistance
Patent Dorothy Hinshaw
Peerreview
Penguins
Persistence
Personalnarrative
Personification
Pets
Photography
Physics
Pi
Pigeons
Pilots
Pinkertonallan
Pirates
Plague
Plains
Plainsindians
Planets
Plantbreeding
Plants
Plastics
Poaching
Poetry
Poisons
Poland
Police
Political-parties
Pollen
Pollution
Polo-marco
Populism
Portraits
Predation
Predators
Presidentialmedaloffreedom
Presidents
Prey
Prey-predators
Prey-predators
Prime-meridian
Pringle Laurence
Prohibition
Proteins
Protestandsocialmovements
Protestants
Protestsongs
Punishment
Pyramids
Questioning
Radio
Railroad
Rainforests
Rappaport-doreen
Ratio
Reading
Realism
Recipes
Recycling
Refrigerators
Reich-susanna
Religion
Renaissance
Reproduction
Reptiles
Reservoirs
Rheumatoidarthritis
Rhythm-and-blues-music
Rice
Rivers
Roaringtwenties
Roosevelteleanor
Rooseveltfranklind
Roosevelt-franklin-d
Roosevelt-theodore
Running
Russia
Safety
Sanitation
Schwartz David M
Science
Scientificmethod
Scientists
Scottrobert
Sculpture
Sculpturegardens
Sea-level
Seals
Seals-animals
Secretariesofstate
Secretservice
Seeds
Segregation
Segregationineducation
Sensessensation
September11terroristattacks2001
Seuss
Sextant
Shackletonernest
Shawneeindians
Ships
Shortstories
Silkworms
Simple-machines
Singers
Siy Alexandra
Slavery
Smuggling
Snakes
Socialchange
Social-change
Socialjustice
Social-justice
Socialstudies
Social-studies
Social-studies
Sodhouses
Solarsystem
Sound
Southeast-asia
Soybean
Space Travelers
Spain
Speech
Speed
Spiders
Spies
Spiritualssongs
Sports
Sports-history
Sports-science
Spring
Squirrels
Statue-of-liberty
STEM
Storms
Strategy
Sugar
Sumatra
Summer
Superbowl
Surgery
Survival
Swanson-jennifer
Swinburne Stephen R.
Synthetic-drugs
Taiwan
Tardigrada
Tasmania
Tasmanian Devil
Tasmanian-devil
Technology
Tecumsehshawneechief
Telegraph-wireless
Temperature
Tennis
Terrorism
Thomas Peggy
Thompson Laurie Ann
Time
Titanic
Tombs
Tortoises
Towle Sarah
Transcontinental-flights
Transportation
Travel
Trees
Trung Sisters Rebellion
Tundra
Turnips
Turtles
Typhoons
Underground Railroad
Us-environmental-protection-agency
Us History
Us-history
Ushistoryrevolution
Us History Revolution
Us-history-war-of-1812
Us Presidents
Ussupremecourtlandmarkcases
Vacations
Vaccines
Vangoghvincent
Vegetables
Venom
Vietnam
Viruses
Visual-literacy
Volcanoes
Voting-rghts
War
Warne-kate
Warren Andrea
Washington-dc
Washington George
Water
Water-currents
Wax-figures
Weapons
Weather
Weatherford Carole Boston
Whiting Jim
Wildfires
Winds
Windsor-castle
Wolves
Woman In History
Women
Women Airforce Service Pilots
Women-airforce-service-pilots
Womeninhistory
Women In History
Women-in-science
Women's History
Womens-roles-through-history
Wonder
Woodson-carter-godwin-18751950
World-war-i
World War Ii
World-war-ii
Wright Brothers
Writing
Writing-skills
Wwi
Xrays
Yellowstone-national-park
Zaunders Bo
ArchivesMarch 2021
February 2021
January 2021
December 2020
November 2020
October 2020
September 2020
June 2020
May 2020
April 2020
March 2020
February 2020
January 2020
December 2019
October 2019
September 2019
August 2019
July 2019
May 2019
April 2019
March 2019
February 2019
January 2019
December 2018
November 2018
September 2018
June 2018
May 2018
April 2018
March 2018
February 2018
January 2018
December 2017
November 2017
October 2017
September 2017
March 2017
The NONFICTION MINUTE, Authors on Call, and. the iNK Books & Media Store are divisions of iNK THINK TANK INC.
a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit corporation. To return to the iNK Think Tank landing page click the icon or the link below. :
http://inkthinktank.org/
For more information or support, contact thoughts@inkthinktank.org
For Privacy Policy, go to
Privacy Policy
© COPYRIGHT the Nonfiction Minute 2020.
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
This site uses cookies to personalize your experience, analyze site usage, and offer tailored promotions. www.youronlinechoices.eu
Remind me later
Archives
March 2023
February 2023
January 2023
December 2022
November 2022
October 2022
September 2022
June 2022
May 2022
April 2022
March 2022
February 2022
January 2022
December 2021
November 2021
September 2021
April 2021
March 2021
February 2021
November 2020
October 2020
September 2020
June 2020
May 2020
April 2020
March 2020
February 2020
January 2020
October 2019
August 2019
July 2019
May 2019
April 2019
December 2018
September 2018
June 2018
May 2018
March 2018
February 2018
January 2018
December 2017
November 2017
October 2017
September 2017



















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
